How to use a welding inverter
The use of inverter sources of welding current (IIST) today almost completely replaces the use of transformer sources, which were their predecessors. At the heart of their principle of action was a step-down transformer operating from a network of 50-65 Hz frequency. He was a rather cumbersome device. To create modern welding inverters, circuit diagrams are used that differ from transformer circuitry.

When using a welding inverter, it is necessary to use MMA coated electrodes.
Each model of inverter is characterized by a suitable circuit solution that provides high-quality design features of the unit. The electrical circuit assumes the operation of the unit on the basis of high frequency pulse converters. The electric arc must be kept for a long time in order for the seam to be very smooth, therefore the very basic electrical circuit allows to produce welding inverters with a light weight, so that they can be held and moved conveniently.
Types of inverter welding current sources
Back to table of contents
Arc, automatic and semi-automatic welding
The market of welding apparatuses supplies not only industry, but also the household sphere, with IIST being used most of all in everyday life. Manufacturers annually supply the latest welding equipment of this type. The high level of demand for inverter devices is due to the use of an electrical circuit based on pulse width modulation. IIST is widely used, which are used for:

Scheme of the device welding inverter.
- Arc welding using non-consumable piece electrodes.
- Semi-automatic or automatic welding.
- Plasma cutting or other types of welding, such as aluminum parts.
Widely used manual arc welding (MMA) using a manual electrode monolith does not require too much power consumption. The device, which has a fairly reduced weight, allows the welder to easily move it closer to the desired connection point. The device of manual arc welding is compatible with the generator, which serves to generate an alternating voltage of 220 V.
The used argon-arc welding (TIG) circuitry of alternating or direct current is associated with advanced features that allow precise control of various parameters of the set mode. For welding, a tungsten electrode is used, which can precisely perform all the work. This allows you to make the appearance of the seam and its quality appropriate. At the same time, the dimensions of the device, its weight, as well as its power consumption, have special advantages.
Semi-automatic welding (MIG / MAG) is associated with the use of a device scheme that ensures the selection of a suitable method for carrying metal. Variants may be associated with drip, jet transfer, etc. This method does not involve the spraying of metal droplets.
Back to table of contentsInverters for plasma arc cutting

Scheme of the welding inverter panel.
A new kind of advanced technology is provided by plasma arc cutting (PAC). The welding process and pauses occur with high arc stability of the inverter apparatus. The cutting process must take place at high speed to obtain a smooth and neat edge that does not require machining.
Some inverters are characterized by self-limiting power, since their action is based on resonant inverters. If you set the device to overcurrent mode, the short circuit will not happen. In general, IIST is a welding machine, the principle of operation of which resembles the action of a computer power supply unit. This is what distinguishes IIST from the classic transformer power supply.
The smaller size of the inverter distinguishes it from the transformer device. At the same time, a high level of frequencies is characteristic of IIST, which exceeds the frequency of operation of a transformer device of 50 Hz. The electrical circuit of the welding inverter provides for operation at frequencies from 55 to 75 kHz.
Back to table of contentsFeatures of the electrical circuit of the welding machine
The inverter, the circuit diagram of which is based on the action of a block of high-frequency transistors (from 55 to 75 kHz), involves the process of switching the input current of high power coming from the diode bridge.

The scheme of the welding inverter.
The element simultaneously serves to rectify the input voltage. After its alignment due to the filtering capacitors, it is possible to obtain a direct current at a voltage of more than 220 V.
The output of the initial stage is associated with the presence of the primary rectifier of the mains voltage (220 V) with an alternating current frequency of 50 Hz. The assembly of this source is made on the basis of a diode bridge, and the capacitor serves as a simple filter. Current limiting after switching on the device is associated with the presence of a non-linear charging circuit. Its main elements are shunt thyristor and current-limiting resistor.
In general, the electrical circuit diagram of an inverter welding machine is associated with the performance of the function of the power source, which ensures the operation of the IIST transistor unit. The action of this block occurs at a frequency of 60-80 kHz, therefore, a step-down transformer operating at the required frequencies is required. This feature allows you to produce welding inverters of a smaller size than transformer devices.
With the smallest size of the modern IIST, in contrast to the transformer apparatus, the power of the device has a constant level. An important step is the solution of the problem associated with the selection of the necessary technology that optimizes the operation of the power unit. It is a constituent element of the electrical circuit of any professional inverter. It is possible to build a power unit on the basis of a topology involving the use of a bridge converter, a single-ended straight-line bridge and half-bridge converter.
Back to table of contents
Description of the principle of operation of the welding inverter circuit
The schematic diagram of the welding inverter can be traced based on the order of actions taken by this device. Initially included in the network device for welding IIST receives alternating current with a voltage of 220 V, the rectification of which occurs when there is a diode bridge in the circuit. To eliminate unnecessary interference in order to protect the high-quality condenser, special interference filters are installed, which are an obstacle.
Then the current is equalized in the presence of a capacitor and is fed to the transistor unit. A current passes through the capacitors, having a voltage higher than that at the output of the diode bridges. The step-down transformer has a winding, where there must be a frequency with which the passage of direct current occurs, several times higher than its original value. As a result, high-frequency alternating welding current is produced at the output.
Next, the current passes through the circuit of the down-frequency high-frequency transformer, which has a secondary winding with a large cross section. At the same time different types of winding materials can be used. The transformer reduces the current to a voltage level of 50-70 V. At the same time, an increase in the strength of the welding current occurs, which exceeds 130 A.
Back to table of contentsThe principle of operation of the output diode
If the assembly is artisanal, then a transformer with a secondary winding made with the use of copper is used (thickness size is 0.3, width is 40 mm). The conditions of this approach are to push the high-frequency current to the surface of conductors whose core is not activated, therefore the device is heated. Next, the resulting current is rectified by the output diodes.
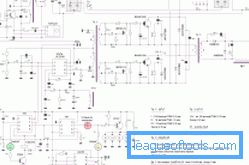
Figure 1. The electrical circuit in which the inverter operates.
A feature of the output diode is its operation at high frequency current, with which not all types of diodes cope. Therefore, you should apply those diodes that are fast. They have a recovery time of no more than 50 nanoseconds.
Under the same conditions, an ordinary diode cannot be used due to the absence of its operation at a high current frequency set. The result is associated with the output of a constant welding current, the strength of which is very high and the voltage low.
Back to table of contentsUniversality of the welding inverter concept
The electrical circuit used to operate the inverter is shown in Fig. 1. Manufacturers provide for any model certain characteristics that allow to increase the reliability of operation of the device and provide safety measures when working with it. The electrical circuit of the device assumes the presence of a thermal control unit, which serves to protect the unit from strong heating and overheating. The unit controls the operation of the cooling system.

Figure 2. The electrical circuit of the welding inverter.
The presence of differences in the details of certain types of welding inverters does not affect the conceptual schemes of their work, which are reduced to the principle described earlier. The equipment in question has an electrical circuit including several important elements. The temperature control unit allows the circuit to control the operation of the ventilation system, which provides forced cooling of the entire unit.
The power transformer of the electric circuit is equipped with a temperature sensor, the type of which is bimetallic and has a fixed response temperature if it reaches 75 ° in the circuit. The heatsink of the power transistor is monitored by an integrated sensor responsible for its temperature.
Back to table of contentsThe possibility of manufacturing inverters based on the concept

Cooking thin metal inverter.
The electrical circuit diagram of the inverter, produced by the domestic manufacturer Resant, allows the company to supply the market with compact units that fit in a case of a not very large size. Despite the different capacities of the devices manufactured by the company, they are characterized by a certain electrical circuit (Fig. 2). It combines the principle of operation of plasma cutters and Resant argon arc welding machines.
The German company FUBAG produces welding equipment of foreign manufacture. It is notable for its special reliability, multifunctionality, being at the same time highly specialized. For welding inverters produced in Germany, there is a large number of functions that are additional. These include forced cooling, low-power operation, microprocessor control, etc.
There are masters for whom the welding inverter assembly does not take a lot of time. You just need to have a basic knowledge of electrical engineering. Schematic diagrams of welding inverters are available if a drawing or instruction is required for independent production. It is important to create a welding inverter, electrical circuit diagrams, which are reduced to obtaining high stability of the welding arc.