How to make the right choice of welding inverter
The invertor welding machine is the equipment which allows to achieve high quality and reliability of welded works even in house conditions. At the same time, simplicity, convenience and ease of its use make the welding inverter one of the most popular devices of this type. However, the choice of welding inverter is quite a challenge, because it must fully comply with the nature of future welding work. In order not to be mistaken and make the right choice, you should consider several of the most important factors at once, namely: functionality, operating conditions of the device, its quality and cost.

Device of the invertor welding machine.
Modes of equipment operation
A welding inverter is a device that allows you to convert an ordinary electrical signal into a different mode required for welding. This signal change is carried out using a special high-frequency converter, that is, an inverter. This makes it unnecessary to use a power transformer during work, which helps to significantly reduce the weight of the welding machine and improves the ability to control the output signal. However, it should be noted that not all welding inverters have the same capabilities, since the operation of this equipment directly depends on the functions and modes that it provides. That is why the choice of the inverter for the house should not be spontaneous, it must be approached wisely.

MMA - welding (manual welding with stick electrodes).
Any welding inverter has a so-called basic mode MMA, in which welding is carried out with conventional coated stick electrodes. Other modes and functions, depending on the model of the equipment, may be present in it either in full or in partial form or completely absent. It is the combination of these indicators that determines the actual operating characteristics of the equipment and has the greatest impact on its cost, which is undoubtedly very important when choosing an inverter for the house.
Back to table of contentsAdditional functions
There are many functions that may be present in a welding inverter for the home, but the most important of them are:
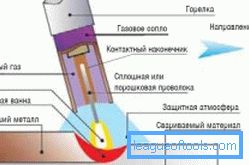
Welding technology.
- Hot Start (which means “hot start”) - this feature provides a short but powerful increase in welding current relative to its normal operating value. This function is intended to accelerate and facilitate the action of ignition of the arc.
- Antistick ("anti-sticking"). During contact of the electrode with the metal surface, when there is a threat of its possible sticking to the metal, an automatic system is triggered, which lowers the welding current to a low value and thus prevents the electrode from melting. If your welding inverter is equipped with a similar function, then you will not need to knock the electrode for a long time just to start the arc, and then tear it off the metal surface, if it has already managed to weld to it. In this case, you can simply put the electrode directly on the metal and without any problems ignite the arc, without even thinking that it can be welded to the metal surface.
- Arc Force ("arc forcing") - this function automatically increases the welding current when a sufficiently large drop of molten metal is separated from the electrode, and also shortens the arc if there is a danger of the electrode sticking to the metal.
- Required availability of AC. Most welding inverters operate on direct current (direct current) (denoted as DC). However, sometimes alternating current, alternating current (AC), has certain advantages over direct welding current, for example, when working with aluminum, when there is a need to destroy the oxide film interfering with welding. Therefore, if the equipment has two welding modes at once, then this greatly expands its functionality and makes it more versatile. However, it should be noted that not all inverters are capable of welding in AC mode, and more precisely, there are very few of them. Determining such a device is not at all difficult; on all welding inverters of this type, manufacturers always write the abbreviation AC / DC.
- TIG mode, which allows welding with a special non-consumable tungsten electrode, as a rule, in an argon environment. TIG welding makes it possible to achieve the highest quality and most reliable weld. In addition, argon welding makes it possible to work with almost all types of metals, regardless of their characteristic properties. Thus, if the inverter is equipped with TIG mode, then this is without a doubt a huge plus for its owner. This type of inverter has only one drawback - it is a high price. But if your financial capabilities allow you to spend a considerable amount of money on the purchase of this welding equipment, then acquire it - believe me, you will not regret it. But it should be immediately noted that the TIG mode can be used for welding metals only if there is a burner, gas fittings and an argon gas cylinder, which will need to be purchased separately.
Contactless arc excitation

Advantages of the welding inverter.
This is a function that allows you to convert a normal current with a low voltage and a standard industrial frequency to a very high voltage of welding voltage of 2500-6000 V and a high frequency from 250 to 300 kHz. This function is provided by such a special device, such as the built-in oscillator, which is not in all welding inverters. Due to the extremely high frequency, even such a large voltage becomes completely safe for a welding specialist. In addition, the oscillator makes it possible to start an arc without even touching the metal surface with an electrode, which is of great importance in performing certain types of work. For example, this is very important when welding stainless steel in TIG mode, as it allows not to contaminate the metal seam with tungsten. In the case when the oscillator is absent in the inverter design, but at the same time any contact of the electrode with the metal surface is strictly prohibited, then the arc should be burned through using a special plate.
Back to table of contentsDecrease the no-load voltage
Current conversion in welding inverter.
Welding in close spaces and in high humidity conditions, for example, in various tanks, wells or tunnels, should be carried out only at low no-load voltage. Standard voltage, which is 50-80 V, at high humidity can be dangerous to the health and life of the welder. In such a situation, only very low voltage, less than 15 V, will be completely safe. To reduce this parameter, special blocks are used to reduce voltage, which, as a rule, are included in the design of the welding inverter. The function of these blocks is to reduce the no-load voltage to non-hazardous indicators for humans, at the moment when the circuit is opened during welding.
Back to table of contentsDigital display
This is a very important function of the welding inverter for the house, which displays all changes in the conditions of welding and thus allows you to control the characteristics of the welding current with high accuracy. Digital display is especially important when there is a need to frequently change welding modes, for example, in the process of working with metals of different grades and thicknesses, when using electrodes of different diameter.
Back to table of contentsThis function will also be very useful for novice welders, as it helps to master the welding business faster and more efficiently, thereby improving their skills.
Rated welding current

The functionality of the welding inverter.
Choosing an inverter for a home in terms of such a parameter as the rated current does not have any particular criteria that would strikingly distinguish it from the choice of any other devices of the same type. However, you should not immediately stop your choice on the purchase of equipment that would exactly match the required parameters, since it would be more correct to purchase a welding inverter with a certain current margin (usually up to 50 A). And for this there are a number of reasons:
- On an unsaturated welding current, you can use your equipment with much greater intensity without any fear that it will overheat.
- When the mains voltage drops to a level of no more than 180 V, the power of the inverter also decreases, and then the welding current is often significantly less than the calculated current.
- When using very long mains (over 15 m) or welding (over 5 m) cables during operation, the welding current indices will also inevitably decrease.
- When buying a welding inverter, you cannot be absolutely sure that the parameters of the nominal welding current indicated on the package really correspond to the real ones. After all, cases where the manufacturer deliberately overestimated the performance of the rated welding current for the purpose of advertising are not rare.
Mains parameters
Welding inverters to a much lesser extent than transformers or rectifiers, depend on the load capacity and characteristics of the supply voltage of the electrical network. As for the devices that are designed to operate from a single-phase network, they, as a rule, calmly withstand voltage fluctuations in the range of 220 V ± 15%. Thus, they can function without any problems at a voltage not exceeding 187 V.
Most modern models of welding inverters, for example, such as the Power Man-D205, can also work perfectly with a drop in electrical voltage of even 20%, that is, at 176 V. In addition, models of a welding inverter for home are being produced today, which fully preserve its performance at very low voltage, not exceeding 140 V. These are the Fast and the Furious-200M, EWM Pico-162 and many others.
In addition, there are models of the inverter welding machine, which are equipped with a special power factor corrector built into their design. This corrector helps them to work even at extremely low voltage, which is only 90 V. These types of welding machines include, for example, "Svarog" ARC 160 PFC.
If the new welding inverter will work from the electric generator, then it is necessary to make the choice of the model of the device, which provides the possibility of functioning from a power source with very low voltage, not exceeding 140 V. Such equipment has reliable protection from any voltage surges. The most popular inverters designed to work with generators are the Wega-200 PFC, Pegas-160E PFC, EWM Pico-180 and many others.