Features and order of performance of pulse welding do it
To date, many welding methods have been developed and successfully commissioned: contact, manual arc, pulse, and even laser welding, as well as a number of highly specialized techniques. Pulsed welding is one of the most effective and modern methods. It involves the use of a special pulsed welding unit. Such welding has been developed as a more versatile and productive alternative to arc welding, which has many drawbacks.

Electric circuit of the household welding machine.
The main parameters of pulse welding
Considering self-welding allows you to get high-quality compounds, mainly steel products and parts from non-ferrous metals. The method is based on the implementation of a short-term welding operation using the energy reserve in the battery or receiver. This receiver is connected to the mains and is constantly charged to a certain value, without overloading the power lines. When welding is performed, the receiver impulses an accumulated energy. So the battery is a kind of smoothing filter, thanks to which the speed and quality of welding increases significantly. Pulsed welding contributes to a significant reduction in the amount of splashing metal flowing from the electrodes.
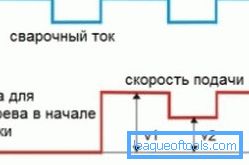
Electrical circuit synchronization of the filing wire feed speed during pulse welding.
If the work will be carried out using non-consumable electrodes, a pulsed arc will control the formation of the welded joint and ensure the most efficient penetration of the metal of the products. When working with a consumable electrode, due to the arc, the melting and transfer of the electrode metal into the seam will be controlled with simultaneous regulation of the splashing of the welding droplet.
Modern pulsed welding machines make it possible to obtain continuous seams by melting individual points with further coating. In the intervals between the pulses, the unit provides support for a low-power arc. The current strength of such an arc is a maximum of 15% of the value of the pulse current. It is necessary to maintain the arc in a steady state.
It is important that the impulse and duty arc be set in the correct ratio. This will ensure the exclusion of craters in the field of welding, reduced area of the required overlap of the connection points and, in general, increased speed.
Back to table of contentsThe concept of "rigidity mode" welding

Electric circuit welding transformer.
“Stiffness mode” is one of the most important technological characteristics of pulse welding. This parameter shows the ratio of the length of the pause to the duration of the pulse.
Under the rigidity of the mode should understand the melting ability of the arc in special pulsed welding machines. By changing the basic parameters of the welding process, the operator can change the shape of the weld pool and its dimensions, control the crystallization process of the metal, form the weld, adjust the limits of deformation, etc.
It is because of the possibility of changing the rigidity of the regime in special welding equipment, the penetrating properties of a pulsed welding arc are most effective when it is necessary to join products from sheet metal with a thickness of 3 mm or less.

Schematic diagram of a pulse welding machine for spot welding.
Pulse welding has proven itself as a method for creating seams of various spatial positions. Thanks to these and other characteristics, pulse techniques are prioritized when performing horizontal and vertical joints, ceiling joints, combining joints on various types of pipes, etc.
As a power source in pulse welding, DC converters are mainly used. Additionally, in the impulse aggregates, sources of the TIR and VSVU series are used.
Earlier it was noted that the battery-receiver helps to ensure uniform load on the phases and at the same time does not create too much load on the network. Such a battery delivers short and powerful impulses to the weld zone. Otherwise, the welding process is performed in almost the same way as any other technology familiar to all welders.
Back to table of contentsPulse welding
The scheme of the weld, performed by pulsed laser welding.
There are several types of pulse welding. Each of them has its own characteristics and purpose. In general, emit:
- Capacitor pulse welding.
- Inertial pulse welding.
- Electromagnetic pulse welding.
- Cordless pulse welding.
Devices for capacitor pulse welding are characterized by a wide variation in the current range. Available in units that support work with low power currents. There are also the most powerful units capable of delivering a current of 100,000 A and even more. The main feature of capacitor pulse welding is that the welding unit allows to achieve accurate dosing of the energy spent on the creation of a welding pulse.
Capacitor pulse welding is performed in a very hard mode. Details are heated by feeding a one-time powerful energy splash. This type of pulse welding is best suited for joining aluminum and stainless steel products.

Options for setting pulse parameters.
The main feature of battery welding is that the design of the welding units used are specific alkaline batteries. They have a special high-strength design and normally tolerate frequent short circuits. Such batteries are characterized by low internal resistance. In the event of a short circuit, devices give a current hundreds of times higher than the standard discharge currents.
Magnetic-pulse welding equipment is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy due to the induction of a magnetic field. Parts of the welded products are fastened under the influence of magnetic forces. In this kind of welding equipment, parts are joined by collisions at the point of contact. High pressure appears, and due to this a welded joint is created.
The principle of operation of inverter pulse units is based on the use of a massive flywheel. It is mounted on one shaft with the generator rotor. Electric motor is used for acceleration. The flywheel accumulates the kinetic energy of rotation, after which, when performing welding directly, the frequency of its revolutions decreases significantly. Due to this, the accumulated energy is recovered in the form of a welding current pulse.
Back to table of contentsThe main stages of the pulse welding process

Comparison of different types of welding.
The technology under consideration is pulsed metal transfer. The use of this technique allows to achieve the highest possible welding parameters. The method combines the best parameters of other existing methods of transfer and is almost completely devoid of the disadvantages of other methods. When using pulse welding, there are no spatter and no fusions are formed.
Pulse devices allow you to cook in any spatial positions. Provides the most efficient and effective wire consumption. The method is characterized by relatively low heat input and allows you to cook products from a variety of different metals.
It is by reducing the heat input achieved the highest possible quality of connection of thin materials without the risk of warping and burn-through.
Welding can be performed with a slower wire feed.

The principle of operation of the welding inverter.
When connecting products using pulse technology, non-contact transfer of the electrode metal into the weld pool takes place. Thus, direct contact of the electrode with the bath is completely excluded. This is made possible by the high speed welding current control feature.
To understand the order of the work, you need to consider the main stages of the process. It all starts with the “hot” phase, during which one drop of metal is formed at the end of the welding electrode. After that, the current is increased to a value that will be enough to drop this drop into the bath due to the effect of compression.
After dropping the drop, the “hot” phase changes to the “cold” one. In the case of a pulsed welding process, the current is reduced to the base one with no need for the power of the welding arc. Thus, the impulse process is not only very efficient, but also relatively cold. When cooking at low currents, the wire heats up, and the arc is maintained, but the amount of energy is not enough to transfer the metal. The duration of the base current is limited so as to prevent the transfer of the metal of the electrode to begin in large drops.
When a metal drop is dropped, the current rises to the maximum value, after which it decreases to the base level, due to which the total heat input decreases. The transfer is controlled by setting the amplitude and duration of the peak characteristic of the welding current.
Pulsed gas shielded welding is one of the most efficient technologies. It is suitable for joining metals of various types and thicknesses. Modern pulse units are very convenient in work. The task of the welder is to install the switch in accordance with the material being processed. At the expense of the source controls, fine-tuning of the process can be carried out. The applied software contributes to the maximum optimization of the welding current profile and saves the welder from the need for complete self-tuning.
Among the main advantages of the method are:
- Top quality welded joints.
- Effective arc control.
- Low processing costs.
Thus, despite the rather high cost of pulsed equipment, such welding is very popular and is often used as an alternative to the classical methods of welding metals in a protective gaseous environment. Most often, the technique is used to connect products from high-quality steel and aluminum.
Work is performed using the minimum set of tools:
- Apparatus for pulse welding.
- Wire and electrodes.
- Protective equipment welder.
Power limitation in pulse welding

The scheme of the pulse power supply.
Spray-free pulse welding has many advantages, but it is not without flaws. The main one is the presence of the performance limit melting metal. The working speed also decreases. Due to the fact that the wire melts intermittently, that is, dropping, melting performance when operating in the traditional mode of pulsed arc welding has an upper limit. After the maximum limit for a wire of a specific diameter is overcome, the gap between the pulses will not be enough to recognize unregulated or adjustable drop separation.
There is a weakening of the process, but it does not go completely into the arc. Welders call this “wire breaking.” Depending on the peculiarities of the upcoming task, the user needs to decide whether it is rational to use welding with minimal spatter, taking into account the speed of the work. It is for this reason that many enterprises are still working with classical welding in a protective gas environment, especially when joining carbon steels.
Thus, pulse welding is one of the most effective and promising methods. If desired, it is mastered and perfectly done by hand, there is nothing difficult in this process.